Age:Mississippian Type designation:Type section: In exposures on a hillslope and in the road ditch north of a secondary road leading to Belknap, about 300 ft (91.4 m) east of Illinois Highway 37 and 0.5 miles (0.8 km) east of the railroad track at Joppa Junction, in SW¼SW¼ sec. 32, T. 13 S., R. 2 E., Dongola quadrangle, Johnson County, Illinois (Swann, 1963, p. 29, 71). History of usage:Named: The Joppa Member was named by Swann (1963, p. 29) and was assigned to the Ste. Genevieve Limestone in some areas and to the Aux Vases Sandstone in others.
Description:The Joppa Member of the Ste. Genevieve Limestone is characterized by limestone and shale with abundant to moderately abundant dolomitic limestone and dolostone beds throughout the subsurface of southwestern Indiana (Droste and Carpenter, 1990). Shales and sandstones are interbedded with the carbonate rocks, including oolitic bodies, in the member, particularly in the western part of the study area (Droste and Carpenter, 1990). The Joppa Member generally ranges from 15 to 35 ft (4.6 to 10.7 m) in thickness (Droste and Carpenter, 1990).
Boundaries:The contact between Ste. Genevieve Limestone and the overlying Aux Vases Member of the Paoli Limestone is conformable generally; however, the contact may be one of minor discontinuity near the outcrop (Droste and Carpenter, 1990, p. 29). Correlations:The Joppa Member of Indiana is equivalent to the Joppa Member of the Ste. Genevieve Limestone of Illinois (Droste and Carpenter, 1990). |
|
Regional Indiana usage:
Illinois Basin (COSUNA 11)
Misc/Abandoned Names:Levias Member (upper part) Geologic Map Unit Designation:Msgj Note: Hansen (1991, p. 52) in Suggestions to authors of the reports of the United States Geological Survey noted that letter symbols for map units are considered to be unique to each geologic map and that adjacent maps do not necessarily need to use the same symbols for the same map unit. Therefore, map unit abbreviations in the Indiana Geologic Names Information System should be regarded simply as recommendations. |
COSUNA areas and regional terminologyNames for geologic units vary across Indiana. The Midwestern Basin and Arches Region COSUNA chart (Shaver, 1984) was developed to strategically document such variations in terminology. The geologic map (below left) is derived from this chart and provides an index to the five defined COSUNA regions in Indiana. The regions are generally based on regional bedrock outcrop patterns and major structural features in Indiana. (Click the maps below to view more detailed maps of COSUNA regions and major structural features in Indiana.) 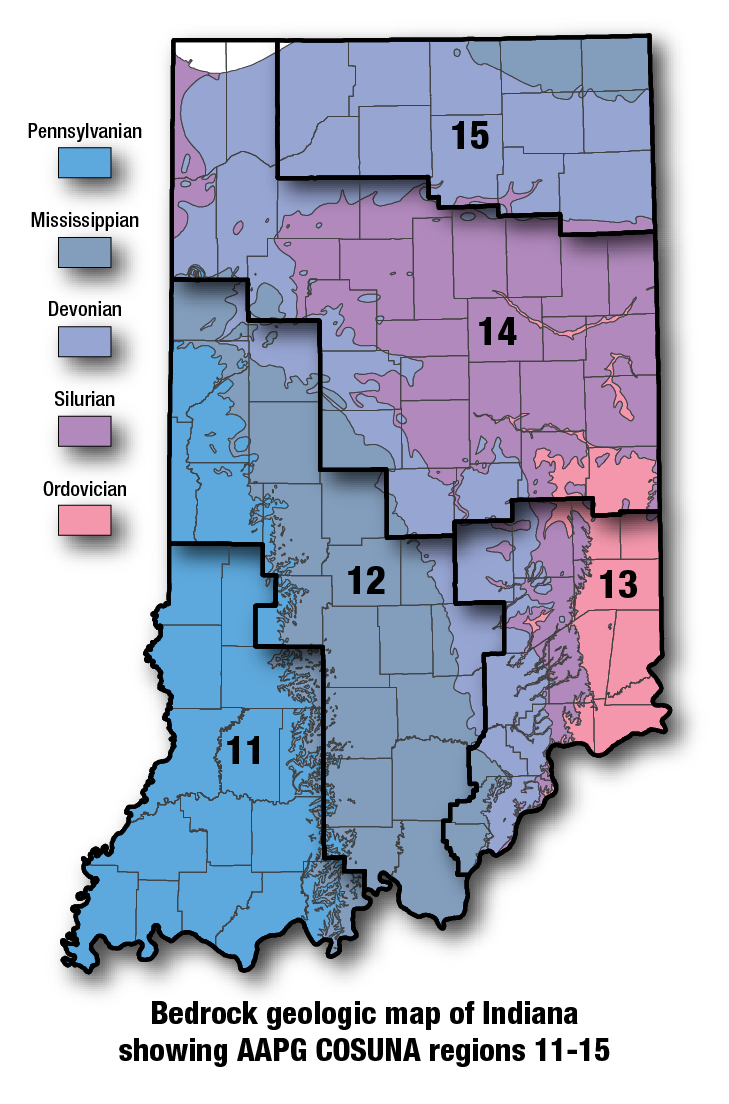
COSUNA areas and numbers that approximate regional bedrock outcrop patterns and major structural features in Indiana. 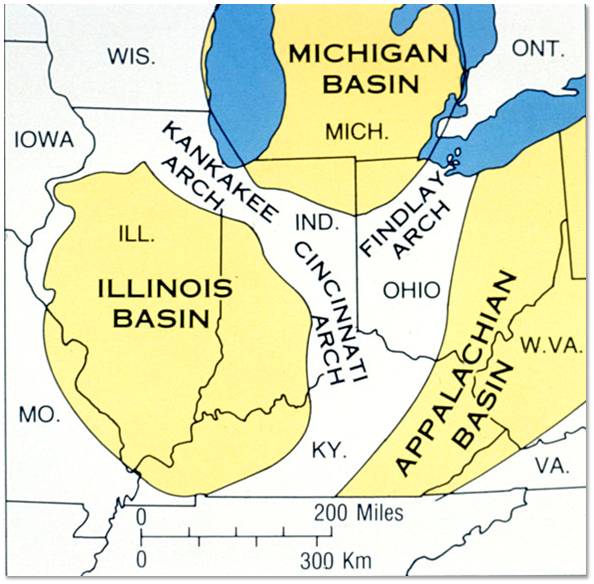
Major tectonic features that affect bedrock geology in Indiana. |
References:Hansen, W. R., 1991, Suggestions to authors of the reports of the United States Geological Survey (7th ed.): Washington, D.C., U.S. Geological Survey, 289 p. Shaver, R. H., coordinator, 1984, Midwestern basin and arches region–correlation of stratigraphic units in North America (COSUNA): American Association of Petroleum Geologists Correlation Chart Series. Swann, D. H., 1963, Classification of Genevievian and Chesterian (Late Mississippian) rocks of Illinois: Illinois State Geological Survey Report of Investigations 216, 91 p. |
|
For additional information, contact:
Nancy Hasenmueller (hasenmue@indiana.edu)Date last revised: February 13, 2013


